TORSADE DE POINTE
Le diagnostic doit être évoqué sur les éléments suivants :
—- PDC, lipothymie, malaise inexpliquées.
—- Trt par diurétique augmentant la kaliurèse, antiarythmique classe 1A ( Quinidiques, RYTHMODAN ), amiodarone, PREPULSID.
—- Bradycardie, ESV post critiques.
BIOLOGIE.
—- Iono à la recherche d’une hypokalièmie, hypomagnésémie.
ECG.
En cours de crise :
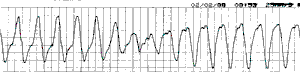
En dehors de la crise :
—- Il peut être normal.
—- Bradycardie +++ si ESV associées.
—- QT allongé +++ si > 0,5 seconde.
—- BAV complet.
CAT.
—- Hospitalisation en urgence par SAMU. Il existe un risque grave surtout s’il existe une cardiopathie sous-jacente.
—- Correction ionique et arrêt du traitement causal.
—- S’il ne cède pas spontanément : ISUPREL 5 amp dans 250 ml de glucosé 5 %
—- Montée d’une sonde EES pour éviter les récidives.
NB : il parait préférable d’éviter le CEE ( choc électrique externe ).
ETIOLOGIES
TDP’s most common etiology is generally associated with a prolonged QT interval. Most frequently, in the critical care setting, this prolonged QT interval is directly attributable to medications the patient is taking. Medications implicated in the development of TDP include:
Antiarrhythmics:
Type IA: quinidine 1.8% to 8%, procainamide, disopyramide
Type IC: encanide,flecainaide
Type III: amiodarone, sotalol, sematilide
Psychotropics:
thioridazine,
haloperidol
Antidepressants: tricyclics
Antihistamines: terfenadine (off the market), astemizole
Antibiotics: erythromycin
spiramycin
pentamidine
sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim
Miscellaneous Medications:
corticosteroids
diuretics (by electrolyte imbalance) +++++
isoproterenol
chloral hydrate
vasopressin, atropine, and others.
Other causes include:
hypokalemia ++++
hypomagnesemia,
hypocalcemia
high-grade AV block
severe bradycardia.